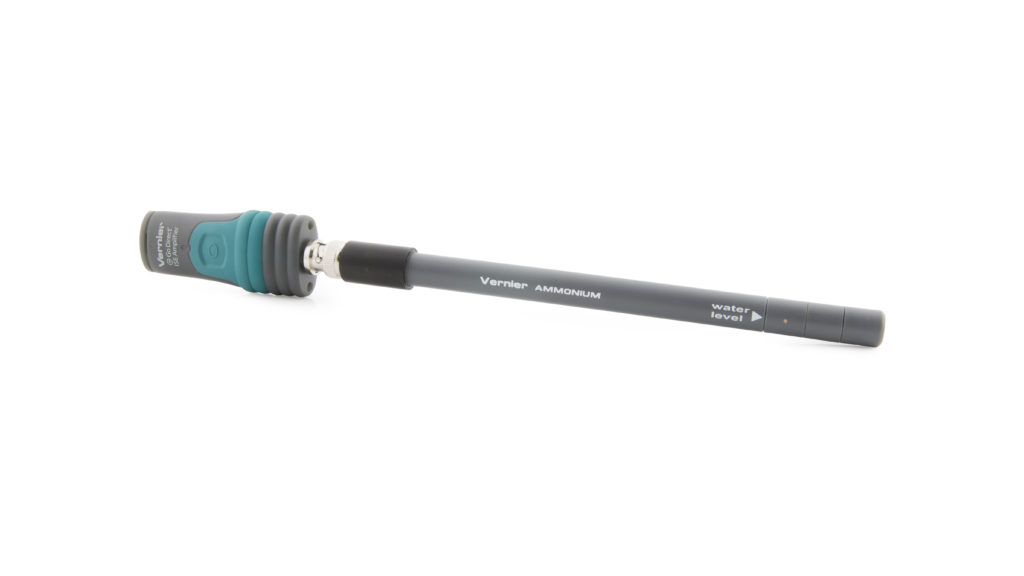
Go Direct® Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode User Manual
Order Code: GDX-NH4
Go Direct Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode (ISE) is used to measure the concentration of ammonium (NH4+) ions in aqueous samples.
Note: Vernier products are designed for educational use. Our products are not designed nor are they recommended for any industrial, medical, or commercial process such as life support, patient diagnosis, control of a manufacturing process, or industrial testing of any kind.
What's Included
- Go Direct Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode (Go Direct Ion-Selective Electrode Amplifier connected to a Go Direct Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode BNC Electrode)
- 30 mL bottle of High Standard solution with SDS (100 mg/L NH4+-N)
- 30 mL bottle of Low Standard solution with SDS (1 mg/L NH4+-N)
- Short-Term ISE Soaking Bottle
- Micro USB Cable
Compatible Software
Choose a platform below to see its compatibility requirements.LabQuest
Interface LabQuest App LabQuest 3 Full support LabQuest 2 Full support 1 LabQuest Incompatible Compatibility Notes
Computers
Software Interface Graphical Analysis Graphical Analysis (Web App) No interface required Full support 1 Full support LabQuest 3 Full support 2 Incompatible LabQuest 2 Full support 2 3 Incompatible Compatibility Notes
Chromebook
Software Interface Graphical Analysis (Web App) No interface required Full support iOS
Software Interface Graphical Analysis Graphical Analysis GW No interface required Full support Full support LabQuest 3 Full support 1 2 Full support 1 2 LabQuest 2 Full support 1 2 3 Full support 1 2 3 Compatibility Notes
Android
Software Interface Graphical Analysis Graphical Analysis GW No interface required Full support Incompatible LabQuest 3 Full support 1 2 Full support 1 LabQuest 2 Full support 1 2 3 Full support 1 3 Compatibility Notes
Python
Software Interface Python No interface required Full support Javascript
Software Interface Javascript No interface required Full support 1 Compatibility Notes
LabVIEW
Software Interface NI LabVIEW No interface required Full support 1 Compatibility Notes
Quick Start: Vernier Graphical Analysis® and Bluetooth®
- Charge your sensor for at least 2 hours before first use.
- Prepare the electrode by soaking it in the High Standard solution for 30 minutes. Refer to the Using the Product section for more information.
- Turn on your sensor. The LED will blink red.
- Launch Graphical Analysis, then click Sensor Data Collection.
- Select your sensor from the list. The sensor ID is located on the sensor label near the bar code. Note: If you don’t see a list of available sensors, click WIRELESS. After selecting your sensor, click Pair.
- Click DONE. You are now ready to collect data.
- For best results, perform a two-point calibration using the High and Low Standard solutions.
Using other Vernier data-collection apps or want to connect via USB?
Visit www.vernier.com/start-go-direct
Note: This sensor also works with LabQuest 2 and LabQuest 3; it does not work with the original LabQuest.
Please see the following link for platform-specific connection information:
Charging the Sensor
Connect the Go Direct Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode to the included Micro USB Cable and any USB device for two hours. Connecting the Go Direct Ammonium Electrode BNC to the amplifier during charging is optional.
You can also charge up to eight Go Direct Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrodes using our Go Direct Charge Station, sold separately (order code: GDX-CRG). An LED on each Go Direct Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode indicates charging status.

| Charging |
Blue LED on steady while sensor is connected to the Micro USB Cable or Charge Station. |
| Fully charged |
Blue LED is off when charging is complete. |
Powering the Sensor
| Turning on the sensor |
Press button once. Red LED indicator flashes when unit is on. |
| Putting the sensor in sleep mode |
Press and hold button for more than three seconds to put into sleep mode. Red LED indicator stops flashing when sleeping. |
Connecting the Sensor
See the following link for up-to-date connection information:
| Connected and charging | Blue and Green LED solid when sensor is connected to Graphical Analysis via USB and unit is charging. (Green LED is obscured by the blue one.) |
| Connected, fully charged | Green LED solid when sensor is connected to Graphical Analysis via USB and the unit is fully charged. |
| Charging via USB, connected via Bluetooth |
Blue LED is solid and green LED is flashing, but the green flashing LED looks white because it is overwhelmed by the blue. |
Identifying the Sensor
When two or more sensors are connected, the sensors can be identified by tapping or clicking Identify in Sensor Information.
Using the Product
- Remove the storage bottle from the electrode by unscrewing the lid and removing the bottle and lid.
- Thoroughly rinse the lower section of the probe using distilled or deionized water.
- Soak the tip of the electrode for 30 minutes in the High Standard solution.
- The ISE should not rest on the bottom of the container.
- The small white reference contacts near the tip of the electrode should be immersed.
- Make sure no air bubbles are trapped below the ISE.
- Connect the sensor following the steps in the Quick Start section.
- For best results, perform a two-point calibration using the High and Low Standard solutions. For calibration instructions, see www.vernier.com/til/4011
- When you are finished making measurements, rinse the electrode with distilled water.
- Slide the cap onto the electrode body, and then screw the cap onto the storage bottle so the tip of the electrode is not touching the sponge.
Important: Do not fully submerge the sensor. The BNC connection is not waterproof.
Important: Do not leave the ISE soaking for more than 24 hours.
Note: If the ISE needs to be transported to the field during the soaking process, use the Short-Term ISE Soaking Bottle. Remove the cap from the bottle and fill it 3/4 full with High Standard. Slide the bottle’s cap onto the ISE, insert it into the bottle, and tighten it. For long-term storage, greater than 24 hours, make sure the sensor is stored in its storage bottle with the sponge slightly damp.
Channels
Go Direct Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode has six sensor channels. The channel names are
- Potential (mV)
- Chloride (mg/L)
- Ammonium (mg/L)
- Calcium (mg/L)
- Nitrate (mg/L)
- Potassium (mg/L)
Note: The Ammonium channel is the default channel for this sensor. All channels are mutually exclusive except Potential (i.e., You can display one concentration channel and Potential at the same time, but you cannot display two concentration channels at the same time). In order to collect data from the other concentration channels, you must also attach the applicable corresponding BNC electrode to the amplifier.
Calibrating the Sensor
A calibration is stored on each sensor before it is shipped. As the membrane ages, this factory calibration may become inadequate. For best results, we recommend performing a two-point calibration.
Note: If you plan to use the electrode outside the range of the standards provided, you will need to prepare your own standards and use those for soaking and calibration. Standards should be two decades apart (e.g., 5 mg/L and 500 mg/L).
For additional calibration information, see www.vernier.com/til/4011
Specifications
|
Range |
1 to 18,000 mg/L (or ppm) |
|
Accuracy after calibration (precision) |
±10% of full scale (calibrated 1 to 100 mg/L) |
|
Interfering ions |
K+, Li+, Na+, Cs+, Mg3+, Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+ |
|
pH range |
2–7 (no pH compensation) |
|
Temperature range |
0–40°C (no temperature compensation) |
|
Electrode slope |
+56 ±3 mV/decade at 25°C |
|
Standard voltages, typical |
High (100 mg/L) 116 mV, Low 0 mV (1 mg/L) |
|
Electrode resistance |
0.1 to 5 MΩ |
|
Minimum sample size |
must be submerged 1.1 in (2.8 cm) |
|
USB specification |
2.0 |
|
Wireless specification |
Bluetooth 4.2 |
|
Maximum wireless range |
30 m |
|
Dimensions |
|
|
Battery |
300 mA Li-Poly |
|
Battery life (single full charge) |
~24 hours |
|
Battery life (long term) |
~500 full charge cycles (several years depending on usage) |
Care and Maintenance
Proper care and storage are important for optimal longevity of your Ammonium ISE.
- Long-term storage of the ISE (longer than 24 hours): Moisten the sponge in the bottom of the long-term storage bottle with distilled water. When you finish using the ISE, rinse it off with distilled water and blot it dry with a paper towel. Loosen the lid of the long-term storage bottle and insert the ISE. Note: The tip of the ISE should NOT touch the sponge. Also, make sure the white reference mark is inside the bottle. Tighten the lid. This will keep the electrode in a humid environment, which prevents the reference junctions from completely drying out. Put the device in sleep mode by holding the button down for at least three seconds. The red LED will stop flashing to show that the unit is in sleep mode. Over several months, the battery will discharge but will not be damaged. After such storage, charge the device for a few hours, and the unit will be ready to go.
- Short-term wet storage (less than 24 hours): Fill the Short-Term ISE Soaking bottle 3/4 full with High Standard. Loosen the cap, insert the electrode into the bottle, and tighten.
Note: Exposing the battery to temperatures over 35°C (95°F) will reduce its lifespan. If possible, store the device in an area that is not exposed to temperature extremes.
Maintaining and Replacing the ISE Standard Calibration Solutions
Having accurate standard solutions is essential for performing good calibrations. The two standard solutions that were included with your ISE can last a long time if you take care not to contaminate them. At some point, you will need to replenish your supply of standard solutions. Vernier sells replacement standards in 500 mL volumes. Order codes are:
- NH4-LST: Ammonium Low Standard, 1 mg/L
- NH4-HST: Ammonium High Standard, 100 mg/L
To prepare your own standard solutions, use the information in the table below. Note: Use glassware designed for accurate volume measurements, such as volumetric flasks or graduated cylinders. All glassware must be very clean.
|
Standard Solution |
Concentration (mg/L or ppm) |
Preparation Method Using High Quality Distilled Water |
|---|---|---|
|
Ammonium High Standard |
100 mg/L NH4+ as N |
0.382 g NH4Cl / 1 L solution |
|
Ammonium Low Standard |
1 mg/L NH4+ as N |
Dilute the High Standard by a factor of 100 |
Replacement Modules
The Go Direct Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode has a PVC membrane module with a limited life expectancy. The module is warranted to be free from defects for a period of 1 year from the date of purchase. It is possible, however, that a membrane module will work well after the warranty period. If you notice a reduced response, then it is probably time to replace the membrane module. Important: Do not order membrane modules far in advance; the process of degradation takes place even when the modules are stored on the shelf.
Battery Information
The Go Direct Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode contains a small lithium-ion battery in the handle. The system is designed to consume very little power and not put heavy demands on the battery. Although the battery is warranted for one year, the expected battery life should be several years. Replacement batteries are available from Vernier (order code: GDX-BAT-300).
Water Resistance
The Go Direct Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode is not water resistant and should never be immersed in water above the BNC junction.
If water gets into the device, immediately power the unit down (press and hold the power button for more than three seconds). Disconnect the sensor and charging cable, and remove the battery. Allow the device to dry thoroughly before attempting to use the device again. Do not attempt to dry using an external heat source.
How the Sensor Works
Combination Ion-Selective Electrodes consist of an ion-specific (sensing) half-cell and a reference half-cell. The ion-specific half-cell produces a potential that is measured against the reference half-cell depending on the activity of the target ion in the measured sample. The ion activity and the potential reading change as the target ion concentration of the sample changes. The relationship between the potential measured with the ISE and the ion activity, and thereby the ion concentration in the sample, is described by the Nernst equation:
- E = measured potential (mV) between the ion-selective and the reference electrode
- Eo = standard potential (mV) between the ion-selective and reference electrodes
- R = universal gas constant (R = 8.314 J mol-1 K-1)
- T = temperature in K (Kelvin), with T (K) = 273.15 + t °C where t is the temperature of the measured solution in °C.
- F = Faraday constant (96485 C mol-1)
- n = valence of the ion
- C = concentration of ion to be measured
- C0 = detection limit
Since R and F are constant, they will not change. The electrical charge of the ion (valence) to be measured is also known. Therefore, this equation can be simplified as
E = Eo – S• log(C + C0)
where is the ideal slope of the ISE.
The following table describes ideal behavior:
| Ion Examples | n (valence of ion) | S (at 25 °C), mV/decade |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium (Ca2+) | +2 | +29.58 |
| Potassium (K+), Ammonium (NH4+) | +1 | +59.16 |
| Nitrate (NO3-), Chloride (Cl-) | –1 | –59.16 |
Assuming C0 is near zero, the equation can be rewritten as:
C = 10˄[(E – Eo) / S]
allowing for the calculation of the ion concentration.
It is very important to note that this table reflects ideal behavior. Ion-selective electrodes have slopes that are typically lower than ideal. It is generally accepted that an ISE slope from 88–101% of ideal is allowable. The slope (S) is an indicator of ISE performance. If the slope changes significantly over time, it may indicate that it is necessary to replace the ISE sensor tip.
Potential vs. Concentration
To measure the mV readings from an aqueous sample, calibration is not required. To convert mV readings to concentration (mg/L or ppm), the software uses a modified version of the Nernst Equation:
C = 10˄[(E – Eo) / Sm]
- C = concentration of ion to be measured (mg/L or ppm)
- E = measured potential of sample (mV)
- Eo = measured potential (mV) at a C = 1 mg/L Ca2+ concentration
- Sm = measured electrode slope in mV/decade
The value of Sm, the measured electrode slope, is determined by measuring the potential of two standard solutions, and solving the equation below:
Sm = – [(Low Standard – High Standard) / # of decades*]
Example Calculation, converting mV to mg/L
For this example, the measured quantities are shown in the chart below:
| Solution | Measured Potential |
|---|---|
|
1 mg/L NH4+ standard |
0 mV |
|
100 mg/L NH4+ standard |
116 mV |
|
unknown sample |
88 mV |
C = 10^[(88 mV – 0 mV) / 58 mV/decade] = 33 mg/L NH4+–N
Ammonium in the Environment
The Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode (ISE) can be used to determine concentrations of NH4+ ions in aqueous solutions, in units of mg/L, ppm, or mol/L. Concentrations of aqueous ammonium ions should not be mistaken for concentration of aqueous ammonia, or NH3(aq). The concentrations of these two species, though different, are often involved in the same equilibrium reaction:
Reaction 1: NH3(aq) + H+(aq) ↔ NH4+ (aq)
In a more acidic environment, higher concentrations of H+ ions will cause this reaction to shift toward the right, resulting in higher concentrations of NH4+. In a more basic (alkaline) environment, the concentration of NH4+ will be lower, causing the reaction to shift toward the reactants, producing higher concentrations of NH3. At pH values greater than 10, most of the ammonium ions will be converted to ammonia. At pH values less than 7.5, most of the aqueous ammonia will be converted to ammonium ions.
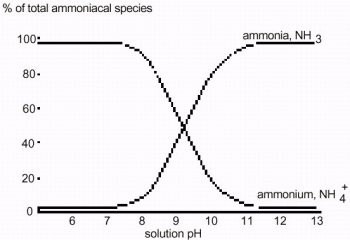
Freshwater Samples for Ammonium Concentration
While permissible levels of ammonium in drinking water should not exceed 0.5 mg/L, streams or ponds near heavily fertilized fields may have higher concentrations of this ion. Fertilizers containing ammonium sulfate, (NH4)2SO4, or ammonium nitrate, NH4NH3, may result in runoff from fields containing higher levels of the ammonium ion, NH4+. Monitoring ammonium levels on a stream that borders fertilized fields may show significant seasonal differences in NH4+ concentrations. In this kind of study, you may also take pH measurements in your water samples; as indicated in the previous paragraph, higher or lower pH values can greatly affect the ratio of NH4+ / NH3 in a sample. Since the Ammonium ISE measures only NH4+ levels, you may want to adjust your samples to the same pH value each time you make measurements; this may not be necessary if you have relatively “hard” water. Hard water is naturally buffered against changes in pH.
Expressing Ammonium Concentration
Concentrations of ammonium are often expressed in units of mg/L NH4+ as N. Here is a calculation for a 100 mg/L NH4+ as N standard solution that is prepared by adding solid NH4Cl to distilled water:
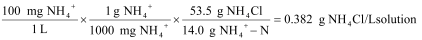
Troubleshooting
Using Ionic Strength Adjustor (ISA) Solutions to Improve Accuracy
For optimal results at low concentrations of ions, a standard method for making measurements with ion-selective electrodes is to add ionic strength adjustor (ISA) solutions to each of your standard solutions and samples.
Adding an ISA ensures that the total ion activity in each solution being measured is nearly equal, regardless of the specific ion concentration. This is especially important when measuring very low concentrations of specific ions. The ISA contains no ions common to the ISE itself. Note: The addition of ISA to samples or standards does not need to be highly accurate. You can add the ISA solution dropwise to a sample using a disposable plastic Beral pipet. We recommend using 0.25 M magnesium acetate solution prepared in 0.5 M acetic acid solution as the ISA for the Ammonium ISE. To prepare this solution, dissolve 53.6 grams of magnesium acetate in sufficient 0.5 M acetic acid solution to make 1.0 liter. Commonly, ISA is added in a 1:50 ratio, or 1 mL of ISA added to 50 mL of water to be tested.
For additional troubleshooting and FAQs, see www.vernier.com/til/665
Repair Information
If you have followed the troubleshooting steps and are still having trouble with your Go Direct Ammonium Ion-Selective Electrode, contact Vernier Technical Support at support@vernier.com or call 888-837-6437. Support specialists will work with you to determine if the unit needs to be sent in for repair. At that time, a Return Merchandise Authorization (RMA) number will be issued and instructions will be communicated on how to return the unit for repair.
Accessories/Replacements
| Item | Order Code |
|---|---|
|
BTL-ES |
|
|
NH4-HST |
|
|
NH4-LST |
|
|
NH4-MOD |
|
|
GDX-NH4-BNC |
|
|
GDX-ISEA |
|
|
CB-USB-MICRO |
|
|
CB-USB-C-MICRO |
|
|
GDX-BAT-300 |
Warranty
Warranty information for this product can be found on the Support tab at www.vernier.com/gdx-nh4/#support
General warranty information can be found at www.vernier.com/warranty
Disposal
When disposing of this electronic product, do not treat it as household waste. Its disposal is subject to regulations that vary by country and region. This item should be given to an applicable collection point for the recycling of electrical and electronic equipment. By ensuring that this product is disposed of correctly, you help prevent potential negative consequences on human health or on the environment. The recycling of materials will help to conserve natural resources. For more detailed information about recycling this product, contact your local city office or your disposal service.
Battery recycling information is available at www.call2recycle.org
Do not puncture or expose the battery to excessive heat or flame.
 The symbol, shown here, indicates that this product must not be disposed of in a standard waste container.
The symbol, shown here, indicates that this product must not be disposed of in a standard waste container.
Contact Support
Fill out our online support form or call us toll-free at 1-888-837-6437.

