Conductivity of Saltwater: The Effect of Concentration
Experiment #17 from Physical Science with Vernier
- Subject
- Physical Science
Introduction
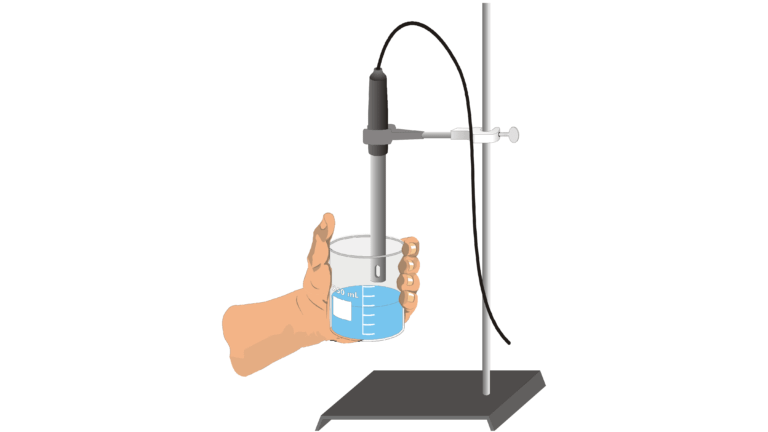
If an ionic solid is dissolved in water, ions are released and the resulting solution will conduct electricity. Dissolving solid sodium chloride (table salt) in water releases ions according to the equation
In this experiment, you will study the effect on electrical conductivity of increasing sodium chloride concentration. Electrical conductivity will be measured as the ion concentration of the solution being monitored is gradually increased by the addition of concentrated NaCl drops. A Conductivity Probe, attached to a computer, will be used to measure electrical conductivity. Conductivity is measured in microsiemens (μS/cm).
Objectives
In this experiment, you will
- Measure conductivity.
- Record data.
- Graph this data.
- Use the data and graph to make conclusions about conductivity.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Option 1

Option 2

Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #17 of Physical Science with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.

