Introduction
Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of individual muscle fibers and has unique properties which allow it to respond to stimuli by contracting. Individual muscle fibers respond to a stimulus (e.g., nerve impulse) with an all or none response, meaning the muscle fiber contracts to its maximum potential or not at all. Once a muscle has contracted, relaxation must occur before it can contract again. There are three basic types of muscle fibers: slow fibers, fast fibers, and intermediate fibers. Fast fibers contract quickly but for a relatively short duration. Slow fibers respond less rapidly, but are capable of a more sustained contraction. The strength of contraction of a whole muscle is dependent on the number of muscle fibers involved.
Objectives
In this experiment, you will
- Obtain graphical representation of the force exerted by your hand while gripping.
- Observe the change in hand strength during a continuous grip over time.
- Observe the change in hand strength during rapid, repetitive gripping.
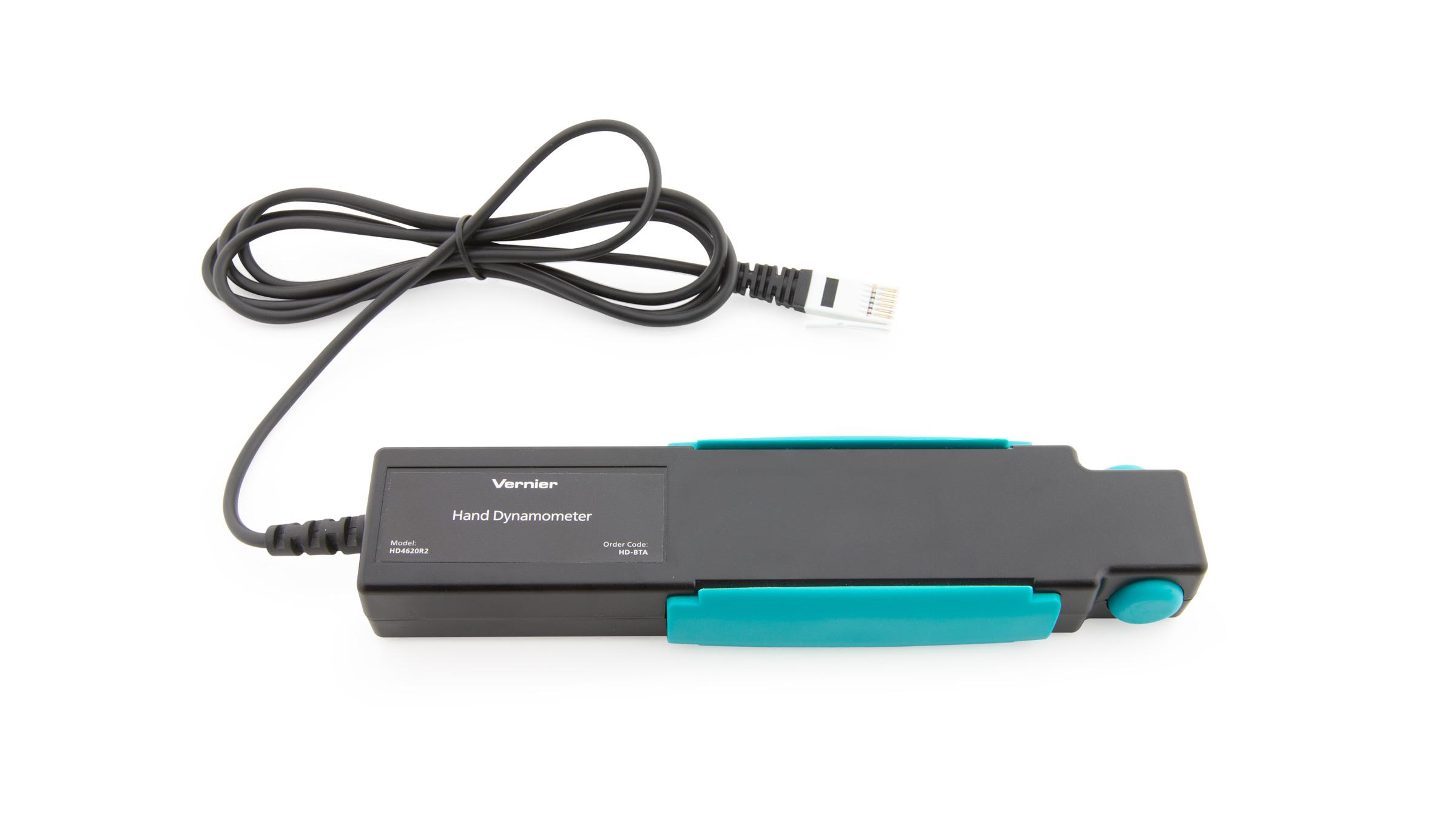
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #17 of Human Physiology with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.


