Introduction
During winter in the Northern Hemisphere, Arctic air temperatures often dip below what we normally think of as the freezing point of water. Yet, while freshwater lakes freeze over, much of the ocean stays in liquid form rather than freezing into ice. Why doesn’t ocean water freeze at the same temperature as fresh water?
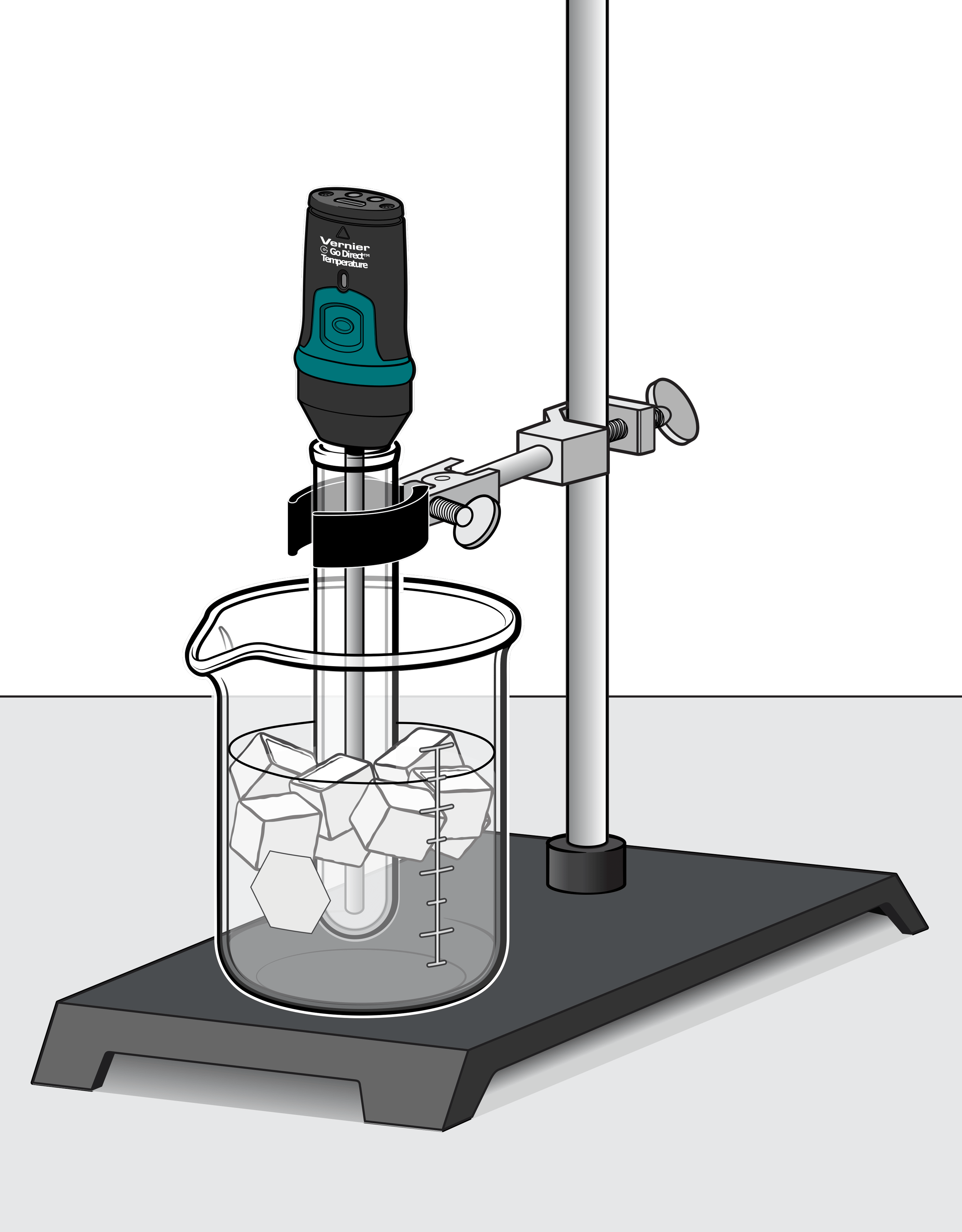
In this experiment, you will use a temperature probe to measure the temperature of water as it cools and then freezes. In Part I, you will collect temperature data as you freeze fresh water in order to determine its freezing temperature. In Part II, you will repeat the experiment with ocean water. You will then compare the two freezing temperatures and hypothesize why they are different.
Objectives
- Observe the freezing of fresh water and ocean water.
- Use a temperature probe to measure temperature.
- Determine the freezing temperature of fresh water and ocean water.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #17 of Earth Science with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.