Another Look at Freezing Temperature
Experiment #3 from Chemistry with Vernier
- Education Level
- High School
- Subject
- Chemistry
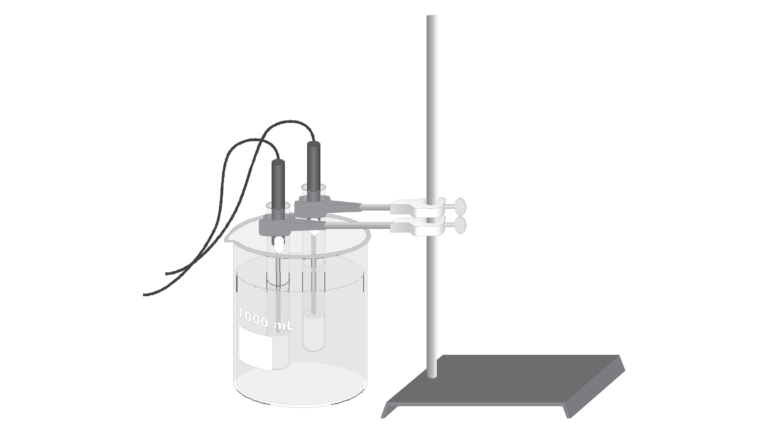
Introduction
In the experiment, “Freezing and Melting of Water,” you saw that the temperature of pure water remained constant at its freezing temperature as it froze and melted. Using a computer-interfaced Temperature Probe, you will now observe what happens when a different pure substance, phenyl salicylate, freezes. Using a second Temperature Probe and sample, you will also see the effect on freezing temperature when a small amount of another substance, benzoic acid, is dissolved in the phenyl salicylate.
Objectives
In this experiment, you will
- Observe what happens when phenyl salicylate freezes.
- See the effect on the freezing temperature when a small amount of benzoic acid is dissolved in the phenyl salicylate.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Option 1
Correlations
Teaching to an educational standard? This experiment supports the standards below.
- International Baccalaureate (IB) 2025/Chemistry
- Structure 3.2.4—Successive members of a homologous series show a trend in physical properties.
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #3 of Chemistry with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.


