
Sharing ideas and inspiration for engagement, inclusion, and excellence in STEM

Photosynthetic organisms such as plants and algae use electromagnetic radiation from the visible spectrum to drive the synthesis of sugar molecules. Special pigments in chloroplasts of plant cells absorb the energy of certain wavelengths of light, causing a molecular chain reaction known as the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. The best wavelengths of visible light for photosynthesis fall within the blue range (425–450 nm) and red range (600–700 nm). Therefore, the best light sources for photosynthesis should ideally emit light in the blue and red ranges. In this study, we used a Go Direct® SpectroVis® Plus Spectrophotometer with a Vernier Spectrophotometer Optical Fiber and LabQuest 2 to collect spectra from four different light sources. This allowed us to determine the wavelengths emitted by each source and to get an idea of their relative intensities.
Wavelengths of light outside of the red and blue ranges are not used by most plants, and can contribute to heat build-up in plant tissues. This heat can damage plants and even interfere with photosynthesis. In order to identify the ideal light source for photosynthesis studies we compared the output or emission spectra of four different E27 type bulbs in the same desk lamp: a) 60 W incandescent bulb, b) 35 W halogen bulb, c) 28 W-equivalent LED “plant bulb” (6–9 W), and d) 13 W compact fluorescent light (CFL) bulb. Each light was measured at a standard distance of 50 cm.
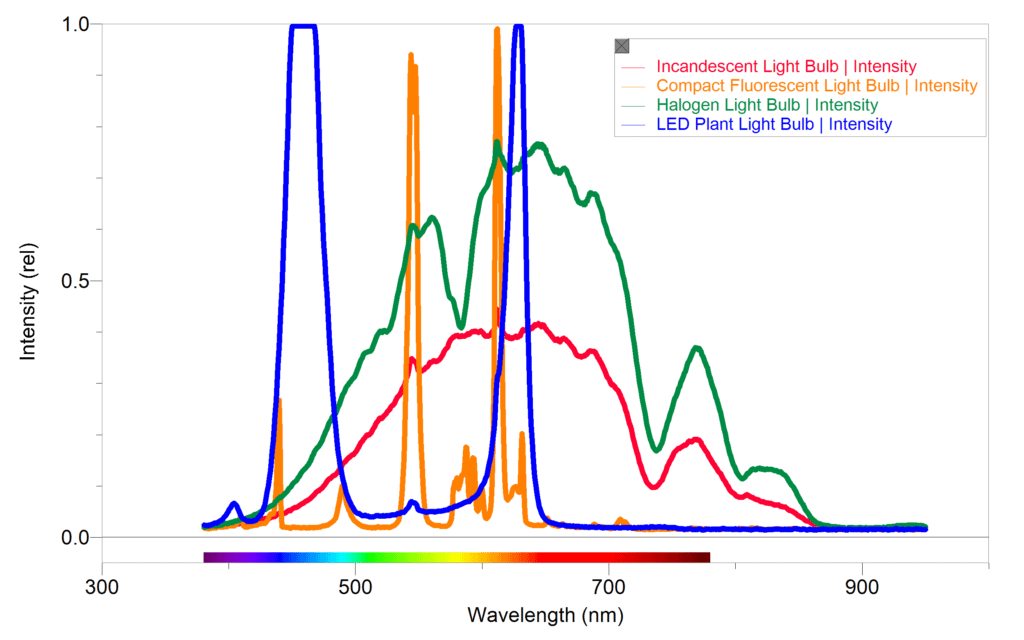
Based on our results, the best light bulb for promoting photosynthesis in plants was the LED plant bulb. This bulb produces a strong output in both the blue and red wavelengths, with very little additional light in other regions to cause heat build-up. All of the other light sources had very little output in the blue range. The halogen and incandescent bulbs had extremely broad output ranges from green to deep into the red portion of the spectrum, but with little to nothing in the blue range. The least suitable lamp for photosynthesis was the CFL bulb. While it emitted some light in both the blue and red ranges (with several peaks in between), the intensity of this bulb was the weakest when compared to all the other lamps. LED plant lights are available from a variety of online merchants and home and garden stores. They have become very affordable, and work well for experiments that investigate photosynthesis.
Share this Article

Sign up for our newsletter
Stay in the loop! Beyond Measure delivers monthly updates on the latest news, ideas, and STEM resources from Vernier.






